
Photobiomodulation or low-level laser therapy in the management of cancer therapy-induced mucositis, dermatitis and lymphedema
Bensadoun RJ. Curr Opin Oncol 2018, 30:226–232
Click to read the abstract
Photobiomodulation or low-level laser therapy in the management of cancer therapy-induced mucositis, dermatitis and lymphedema
Bensadoun RJ. Curr Opin Oncol 2018, 30:226–232
PURPOSE OR REVIEW:
There is a large body of evidence supporting the efficacy of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) also known as PhotoBioModulation (PBM) when used for the prevention and/or treatment of oral mucositis in patients undergoing radiotherapy for head and neck cancer, or high-dose chemotherapy regimens. This review aims at giving the state of the art of this technique in this indication.
RECENT FINDINGS:
Recent advances in LLLT/PBM technology, together with a better understanding of mechanisms involved and dosimetric parameters may lead to the management of a broader range of complications associated with cancer treatment. This could enhance patient adherence to cancer therapy, and improve quality of life and treatment outcomes.
SUMMARY:
The article discusses LLLT/PBM mechanisms of action, dosimetry, and safety, and aims to identify some cancer treatment side-effects for which LLLT/PBM may prove to be effective (oral mucositis, radiation dermatitis, lymphedema). In addition, LLLT/PBM parameters for each of these complications are suggested and future research directions are discussed.
Main findings
- Interesting information on dosage for radiation dermatitis that is relevant for lymphoedema practitioners.
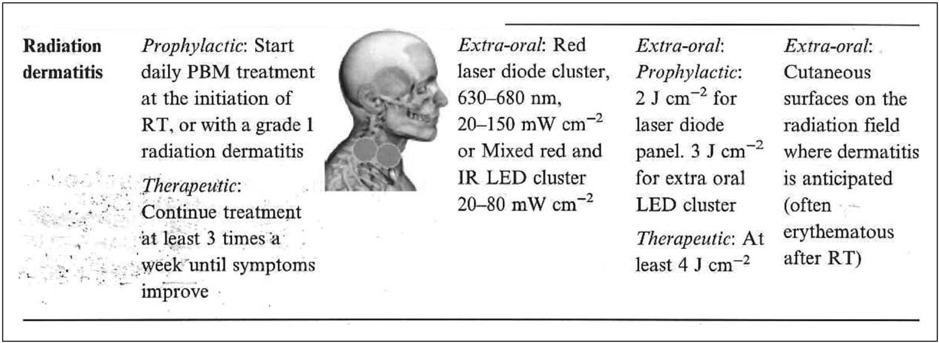
FIGURE 2. Radiation dermatitis: proposed PBM treatment parameters. PBM, PhotoBioModulation. permission
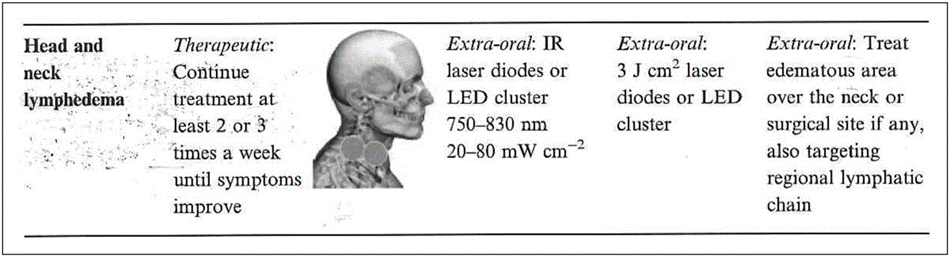
FIGURE 3. Head and neck lymphedema: proposed PBM treatment parameters. PBM, PhotoBioModulation.
- It seems reasonable to assume that LLLT/PBM may reduce the severity and/or prevalence of radiation dermatitis.
- LLLT/PBM has shown effectiveness in the management of oral mucositis, radiation dermatitis, lymphedema, and elicits several potentially beneficial effects, including reduction of inflammation and pain, promotion of tissue repair, reduction of fibrosis, and protection and regeneration of nerves.

