Resources for Lipedema

New Insights on Pathophysiology and Treatment of Lipedema
July, 2020
Dr Karen Herbst
Hosted by Lympha Press
Dr. Karen Herbst, Board Certified Endocrinologist and lipedema specialist physician, discusses the latest on pathophysiology and treatment of lipedema, and answers listener questions.
The video includes:
Discussion of lipedema as disease of loose connective tissue and explores in detail the types of connective tissue.
Lipedema includes both fibrosis and oedema.
Hand and feet are unaffected.
Different from lymphoedema in that free fluid is not visible but there is a risk for lymphedema
Lipedema is not always painful.
The presentation reviews lipedema presentations
There is inflammation that results in fibrosis and there is necrosis of fat cells/
Fibrosis inhibits fat loss after bariatric surgery and lipedema tissue is highly resistant to loss by bariatric surgery.
There is a discussion on bound and free fluid and how it relates to lipedema and lymphoedema.
Extracellular water is higher in loose connective tissue (LCT) of women with lipedema.
Sodium (Na+) content is elevated in the skin and LCT of women with lipedema.
There are dilated blood and lymphatic microvessels, angiogenesis, increased macrophages and adipocyte hypertrophy in lipedema thigh skin and fat tissue.
VEGF levels are higher in women with lipedema. VEGF induces formation of leaky vessels.
Macrophages are higher in skin and LCT of women with lipedema. Macrophages repair and inflame tissue.
50% have hypermobile joints
Lipedema treatable things:
- Fibrosis
- Free fluid
- Glycosaminoglycate (GAG) bound fluid
- Pain
Things to consider
- Skin folds
- Lobules
- Pain
- Genu valgum
- Ankle pronation
- Numbness
Have a low salt diet
Avoid corticosteroids
Eat anti-inflammatory foods. Avoid processed foods
Anti-inflammatory supplements may be useful:
- Diosmin
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
Pumps improve the extracellular matrix. They mechanically stimulate connective tissues, improve fluid and GAG flux, and reduce fibrosis.
External forces on tissue improve extracellular matrix (ECM)
- Stretching pre-adipocytes inhibits them from becoming adipocytes
- Energy is spent on ECM remodelling/healing, not fat storage.
The PsychoSocial, Clinical and Dietary Impacts of Lipoedema
June, 2020
Dr. Catherine Seo , Dr. Matthew Carmody and Leslyn Keith
Hosted by Lympha Press
The speakers include:
- Dr. Catherine Seo is a world leader in psychosocial counseling in the field of lipoedema and discusses the psychosocial aspects of living with lipoedema.
- Dr. Matthew Carmody discusses the differential diagnosis of lipoedema and obesity.
- Leslyn Keith, a lymphedema and lipoedema specialist, and researcher presents the Ketogenic Diet for Lipoedema.
Some highlights include:
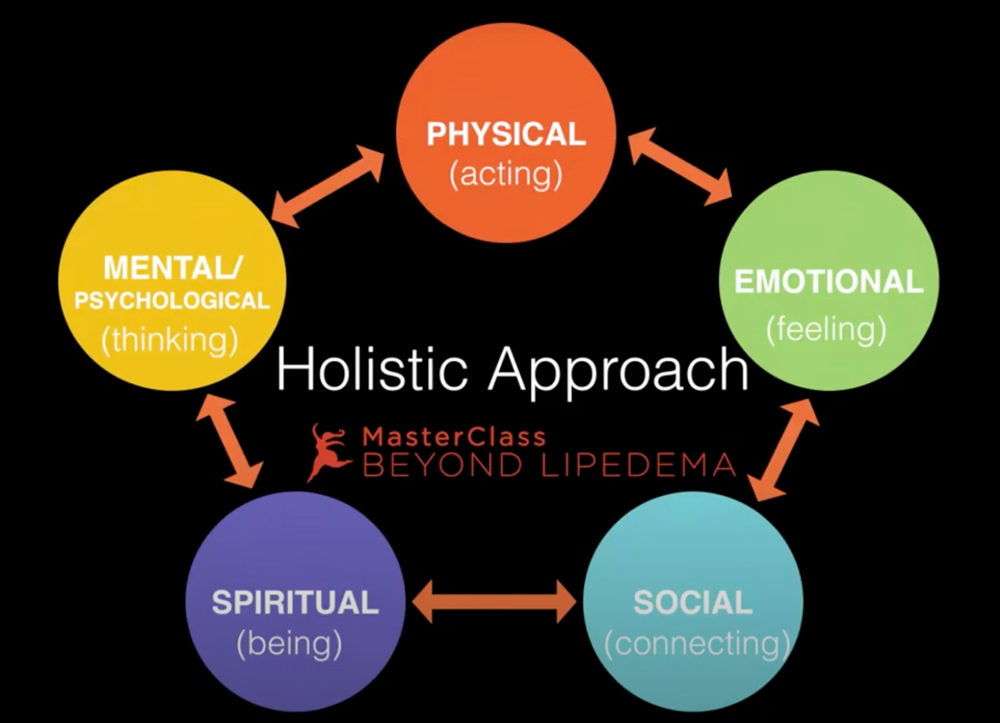
- Lipedema requires a holistic approach that includes the following areas.
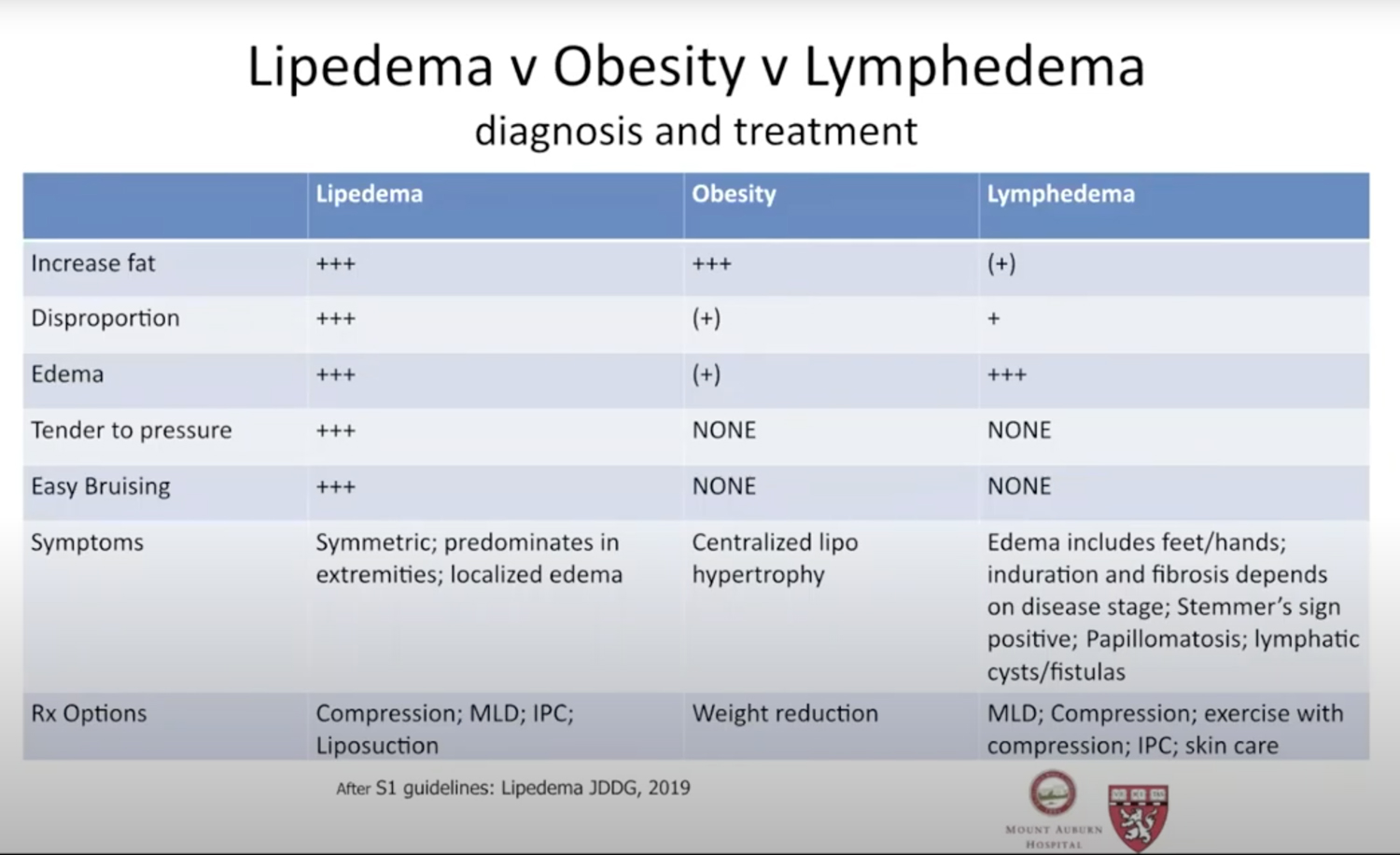
Differential diagnosis refer to the table below.
An explanation of lipedema interstitial edema.
- There is an increased capillary leak with angiogenesis and dense clusters of dilated capillaries
- Increased interstitial fluid leading to adipocyte hypertrophy/growth
- Increased macrophages with inflammation leading to fibrosis and nerve pain
- Expansion in lymphatic vessel size (area) and area/perimeter ratio (but without a change in transport leading to increased lymphedema risk)